…and their conduct in the Facebook matter is damaging to the profession of the law.
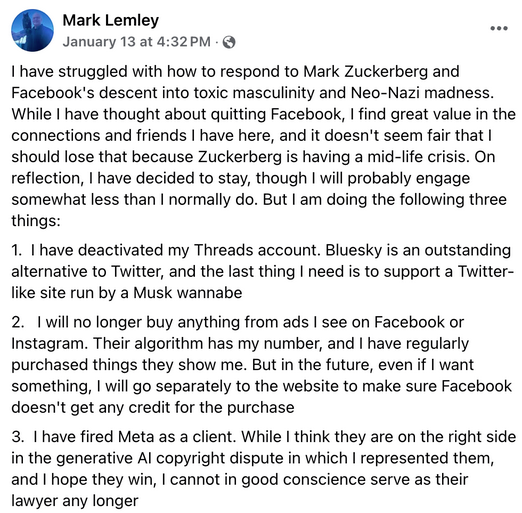
Intellectual property expert Mark Lemley, a professor at Stanford Law School and a partner at law firm Lex Lumina, represented Facebook in the copyright case brought on behalf of creators claiming the platform infringed their intellectual property. Yesterday he “fired” his client, despite believing that Meta’s case was strong. His stated reason was that he is outraged at Mark Zuckerberg and Meta’s “descent into toxic masculinity and Neo-Nazi madness.” His law firm then proceeded to back him up.
Here is Lemley’s Facebook post announcing his decision:
Meanwhile, the managing partner of his woke law firm followed with the statement that “Money can’t buy everyone. We’re proud to be a firm that doesn’t sell out our values. Sadly, it seems this is becoming a rarer and rarer quality in America today.” Another partner said, “When we started Lex Lumina, one of the things we committed to was only taking cases we felt good about, on the law and in terms of who we represented. Proud to be working with my friend and partner, Mark Lemley, who lived out our commitment today.”
This is labeling unethical lawyer conduct as ethical.
Lemley went on to post a reiteration of his decision on LinkedIn. It wasn’t “the right call.” If Lemley and his firm had refused to represent Meta in the case of Kadrey v. Meta Platforms initially, there would be no ethics foul: nothing in the Rules of Professional Conduct mandates that any lawyer accept any client, although the traditional ethos of the profession strongly encourages lawyers to do so. However, dropping a client because of what that client has done or said that has nothing to do with the case of the representation, while not a strict rules violation, is unprofessional and creates a dangerous slippery slope…one that many in the legal profession have been leaping down in recent years.
Noteworthy is the fact that Lemley is no legal ethics expert. His actions demonstrate that vividly, and his post is a flashing sign stating, “I am biased, Trump Deranged, a Democrat, and believe in good censorship.” Got it, Professor.
Naturally, the woke legal hacks at Above the Law love this, and ratioanalizes it with an argument that has been rife since the corrupted legal profession started behaving like the restaurants who won’t serve people wearing MAGA caps. Joe Patrice, the head ideologue at Above the Law writes,
A sanctimonious segment of the legal profession harps on the idea that “everyone is entitled an attorney.” Except no one is entitled to you as an attorney. Frankly, no one is entitled to anything in a civil case and to the extent society needs to extend more protections to indigent clients on the wrong end of life-altering civil actions — landlord-tenant cases for instance — there’s definitely no such entitlement for a multibillion-dollar company in a copyright dispute.
Representing a client is a business decision. Some lawyers thrive as counsel of last resort and model their business around the willingness to represent unpopular clients. Other lawyers build their business on crusading for good causes. A whole lot of lawyers exist somewhere between those poles. In fact, a lot of deep-pocketed clients also don’t want to work with firms associated with unpopular causes — that’s a business decision too.
There’s nothing wrong with any of these approaches. Lawyers should feel free to build their practice however they want.
What is wrong with that argument is that it violates Kant’s Rule of Universality, the “What if everybody did it” test that is part of the philosopher’s categorical imperative. Patrice’s standard, and accepting Lemley’s conduct, would mean that certain citizens and organizations could be left without legal representation entirely because they were regarded by a politicized legal profession (and an ethically addled public) as “bad.” While it is accurate to assert that the Sixth Amendment does not guarantee a citizen legal representation in a civil (as opposed to a criminal) case, the legal professional has long embraced the principle that the same ethical and practical justifications should apply. If we accept Patrice’s ethically ignorant (or deliberately misleading) argument that whether to accept a representation is purely a business decision, that allows lawyers and firms to avoid unpopular clients, leaving them potentially at the mercy of the polls and bias in a rigged legal system.
This is what the actions of Lemley and his firm are pointing to. It is the reason Donald Trump has had difficulty hiring lawyers and getting competent legal assistance. Firms and lawyers get threatened by clients, and in the constant tug-of-war between the profession of law and the business of law, business now prevails. Once, before the progressive bias in laws schools and among lawyers became the status quo, the mission of representing unpopular causes and clients, even when the attorneys for these clients personally disagreed with and even deplored their conduct was seen as part of the legal profession’s mission. Wall Street lawyers represented accused terrorists after the bombings of 9/11 after public figures called for their firms to be boycotted. When Coca-Cola virtually extorted their law firm into dropping its representation of the House Committee defending the Defense of Marriage Act before the Supreme Court, the partner handling the case, Paul Clement, wrote in his letter of resignation in protest of the decision, that “defending unpopular positions is what lawyers do.” Similarly defending unpopular clients is what lawyers must do and be honored for, or we have no longer have an equitable legal system.
The unethical principle Lemley is advocating is worse than opposing taking on an unpopular position: he seeks to justify abandoning a position he feels is valid because his client’s policies no longer please him. I have vowed to promote this section of the Rules of Professional Conduct because it is such a crucial one for maintaining the integrity of the profession and trust in its members:
“A lawyer’s representation of a client, including representation by appointment, does not constitute an endorsement of the client’s political, economic, social or moral views or activities.”
It should be obvious that if it becomes acceptable for lawyers and firms to refuse representations because they fear being regarded as endorsing a clients’ “political, economic, social or moral views or activities,” the legal profession will have nullified that critical standard in practice, and the public will be correct to assume that if a lawyer or firm represents an unpopular cause or individual, those lawyers agree with and endorse them. This is what ideologues like Joe Patrice want, a legal system as polarized as the political system, where one can tell the “good” lawyers from the “bad” lawyers by whom they choose to represent.
Dropping a client one has already accepted, which is what Lemley has done, is worse still. In his letter excoriating his former firm, Clement quoted Griffin Bell, a judge and former U.S. Attorney General, declaring that once a lawyer has accepted a case, it is the lawyer’s duty and ethical obligation to continue the representation. In 2011, when the DOMA controversy erupted, Clement’s position was almost unanimously praised within the profession. Theodore Olson, the late conservative attorney, praised Clement’s “abilities, integrity, and professionalism”.” Olson, who like Clement was a solicitor general during the George W. Bush administration and was a successful Supreme Court advocate, told the media, “I think it’s important for lawyers to be willing to represent unpopular and controversial clients and causes, and that when Paul agreed to do that, he was acting in the best tradition of the legal profession.” Seth Waxman, who served as solicitor general during the Bill Clinton administration, said, “I think it’s important for lawyers on the other side of the political divide from Paul, who’s a very fine lawyer, to reaffirm what Paul wrote. Paul is entirely correct that our adversary system depends on vigorous advocates being willing to take on even very unpopular positions.” In approving Clement’s stand, The Washingtonian observed, “There are countless examples of law firms taking on and standing by controversial clients, even at the risk of their public images.” There are fewer and fewer examples now, however. This is the dystopian legal landscape that Lemley and his firm are promoting, and it is an unethical one.