[The Supreme Court came down with four controversial and ideologically contentious decisions in June, and I apologize for taking almost a month to cover them all. One of the reasons Ethics Alarms occasionally launches a series like this one is to ensure that developing ethics stories of importance do not push important issues to the sidelines. The fact that this four part series had only finished parts 1 and 2 was an irritant to me, as well as some readers.]
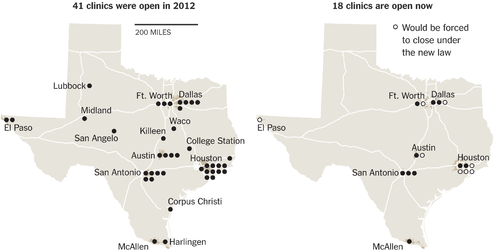
In Whole Woman’s Health v. Hellerstedt, decided on June 27, the Supreme Court held in a 5-3 majority that two provisions of a Texas law, one requiring physicians who perform abortions to have admitting privileges at a nearby hospital and another requiring abortion clinics in the state to have facilities comparable to an ambulatory surgical center, places a substantial and unconstitutional obstacle in the path of women seeking an abortion, because they constituted an undue burden on abortion access.
Life would be so much simpler if our elected officials and activists employed an adaptation of the Golden Rule, and looked objectively at issues from the other side’s point of view. This is especially true in the realm of rights. Second Amendment absolutists insist that virtually any laws regulating who can purchase guns, when and where they can purchase them, and how and how quickly they can be purchased are efforts to whittle away the right to bear arms. They also argue that such regulations have the ultimate goal of eliminating that right entirely, which, in many instances is the case, especially if you listen carefully to the rhetoric of the legislators proposing such measures. There is little difference from this and what anti-abortion advocates are attempting to do with laws like House Bill 2 (H. B. 2).
The bill ostensibly is designed to make abortions safer, thus protecting women’s health, just as many gun laws are promoted as safety measures. Oddly, virtually all of the supporters of the Texas bill would make abortion illegal if they could. I’m sure it’s just a coincidence, just as it’s a coincidence that the authors of bills requiring potential gun owners to jump through increasingly burdensome hoops and deal with mandatory trigger locks and “safe gun” technology would gladly repeal the Second Amendment if they could. The ethical principle is the same in both matters: a right isn’t a right if legal obstacles make it difficult to exercise that right.
The question is, what’s a reasonable obstacle? Any regulation imposed on a constitutional right must not create “a substantial obstacle” and must be reasonably related to “a legitimate state interest.” The Supreme Court uses the language and logic of case precedents, which are its previous examinations of these issues and the balancing they require. One such case, though I did not find it mentioned in the majority opinion or dissents in Hellerstedt, would be the voter ID decision of many years ago, in which a strong majority ruled that the state interest in preventing fraudulent voters and maintaining the integrity of the election process justified inconveniencing those who were subjected to the extra burden of obtaining appropriate identification. In recent years, this decision has been questioned because many believe the motive behind voter ID laws is not really to protect the franchise, but to keep likely Democratic voting blocs from the polls.
Is there a difference legally between a bill that is authored with the intent to restrict the right to vote of older, poorer, and darker citizens while claiming that its sole purpose is to make sure non-citizens don’t affect the results of elections, and an identical bill that is genuinely intended to safeguard the voting rolls, without any political motive at all? No, or at least there shouldn’t be. The Court’s job is to evaluate what the law does, not try to read the minds and hearts of those who wrote it. Justices only should try to do the latter when there is a debate over what the law says.
Ethically, however, there is a significant difference between a law using a public purpose as a sham to accomplish unethical ends, and a law with a legitimate purpose that has some negative side effects. Trying to restrict a citizen’s rights because one doesn’t respect those rights (or perhaps the citizen) is unethical.
The SCOTUS majority, in its typical examination of a balancing case like this, looked at whether there was a sufficient public safety benefit to a law that had resulted in a precipitous reduction in abortion services: Continue reading