Last year, when I noted this story in the December 23 warm-up, I was asked if there would be more on the topic. Here is more. It deserves it.
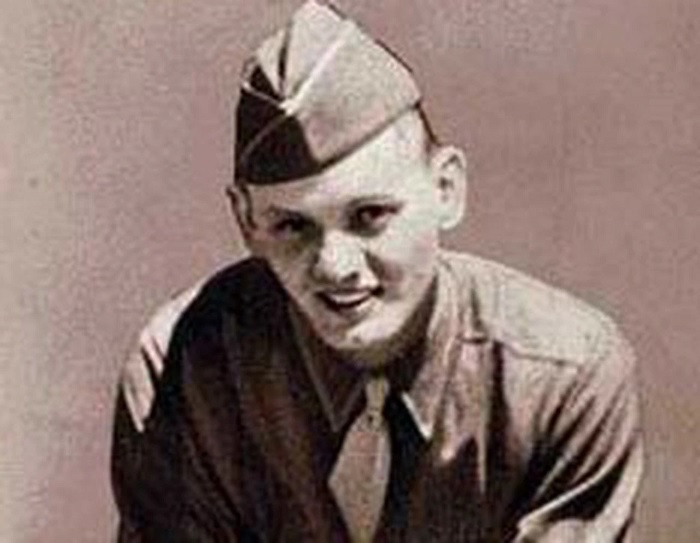
During World War II, U.S. Army Pvt. Eddie Slovik was tried for desertion. On this date in 1944 he was found guilty in his court martial and condemned to death by firing squad. It was the first such sentence against a U.S. Army soldier since the Civil War, and Slovik was the only soldier executed for desertion in World War II. In the intervening years between then and now, his death has become a point of ethical controversy, never resolved, and generally debated before the public from an emotional rather than an ethical, legal or even a military perspective.
I was first told the story of Eddie Slovik by my father, a decorated army veteran and officer during the war. A fervent admirer of General Eisenhower, he still disagreed with Ike’s much criticized decision to allow Slovik’s execution by firing squad to go forward. Dad was not supportive of the command principle of using a particularly blatant example of a crime to send a message to others considering similar conduct, and having had several Eddie Sloviks to contend with under his command, he did not like the resolution of the Slovik dilemma.
I argued the point with him many times over the years. “The question isn’t whether it was fair for Slovik to have been shot,” I told him. “It was. The question is whether many more deserters should have been shot as well.”
Private Eddie Slovik was a draftee, and not a good bet to be a good soldier. He had been classified 4-F because he had spend time in prison for a felony (grand theft auto), but was deemed draftable as the Allied war effort required quantity even more than quality as the conflict dragged on. He was trained to be a rifleman, though Slovik claimed that he hated guns.
In August of 1944, the Army shipped Slovik to France to fight with the 28th Infantry Division, which had suffered massive casualties. When he experienced being under heavy fire for the first time, Slovik concluded that he would not make it in combat. Though the current trend is to say that he and a friend “got lost,” it seems more likely that they were hiding before they turned themselves in to the Canadian military police. The Canadians returned the two to the Americans after about a month and a half.
Slovik asked the company commander if “getting lost” again would be considered desertion. Despite being warned that it would be, he went AWOL, then the next day turned himself in at a nearby field kitchen. He handed the cook this statement:
Continue reading →